Macau's Shift to General Public Players Linked to Rising Gambling Issues

Photo by Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
Key Takeaways
- Casino exclusion applications surged by 67.9% last year
- Self-exclusion requests reached 828, up 74.3% from 2024
- Third-party applications for exclusions increased by 34.8%
Macau's Gaming Inspection and Coordination Bureau (DICJ) reported a significant increase in casino exclusion applications last year, rising by 67.9% to a total of 952. This marks a notable jump from 567 applications in 2024, excluding court-ordered exclusions. Self-exclusion requests accounted for the majority, with 828 cases, reflecting a 74.3% increase from the previous year.
Third-party applications, which require confirmation from the individual, also saw growth, increasing by 34.8% to 124. These figures show a growing trend of locals seeking to distance themselves from gambling despite an increasing focus on the mass market.
Market Shift
Macau's growing problem with gambling is a trend that follows the shift by casinos from catering to VIPs and high rollers to attract the premium-mass market and general public.
In 2025, the region's six gaming operators collected a record gross gaming revenue (GGR) of US$30.9 billion, the highest since 2019.
However, the landscape of revenue generation has changed significantly after COVID-19. The Chinese government, under President Xi Jinping, dismantled the VIP junket model, which had previously facilitated high-stakes gambling by wealthy mainlanders. The crackdown was part of efforts to curb illegal cash flows, significantly altering Macau's gambling environment.
Nongaming Investments
To secure 10-year extensions of their casino licenses, Beijing and Macau compelled major operators like Sands, Wynn, and MGM to invest US$16 billion in nongaming initiatives. This strategy aims to transform Macau from a high-stakes gambling destination into a more diverse destination for leisure, family vacations, and business.
As a result, VIP gambling rooms have diminished, and casinos are now broadening their marketing efforts. However, Macau officials note that this shift has also contributed to rising gambling issues. In 2025, 828 individuals opted for self-exclusion, a significant increase from 475 in 2024, highlighting growing concerns over gambling addiction.
Regulatory Framework for Exclusions
Law No. 10/2012 serves as the foundation for Macau's self-exclusion program, granting the DICJ authority to implement prohibitions following requests. Changes introduced in December 2019 expanded these regulations, imposing a citywide ban on casino employees' gambling outside their workplaces. Alongside existing rules, the two-year limit on exclusions is designed to be temporary and effective, allowing individuals to request revocation if their situations change.
Lucas Michael Dunn is a prolific iGaming content writer with 8+ years of experience dissecting it all, from game and casino reviews to industry news, blogs, and guides. A psychology graduate and painter that transitioned into the iGaming world, his articles depend on proven data and tested insights to educate readers on the best gambling approaches. Beyond iGaming content craftsmanship, Lucas is an avid advocate for responsible play, focusing on empowering players to strike a balance between thrill and informed choices.
Related News

Gambler who lost £250,000 says he “suffered in silence” before seeking help
A man from Bedfordshire who lost more than £250,000 through gambling has spoken publicly about his addiction after completing residential treatment with gambling harm charity Gordon Moody.
How UK regulation is shaping the future of European iGaming
As more European countries regulate online gambling, many are looking to the UK’s regulatory framework for guidance. The Gambling Commission’s approach to enforcement and consumer protection is increasingly influencing how operators build platforms and manage risk across the continent.

Maryland Senate Does Not Vote On Proposals to Legalize Online Casinos
This is the third straight year that Sen. Ron Watson (D-23) has attempted to get a form of iGaming legislation over the line.

Hoiana Hotel & Suites Earns Forbes 4-Star and Unveils Entertainment Hub
Forbes Travel Guide awards Hoiana Hotel & Suites a 4-Star rating as the resort launches a new Entertainment Hub with bowling, VR sports, arcade games, and nightlife.
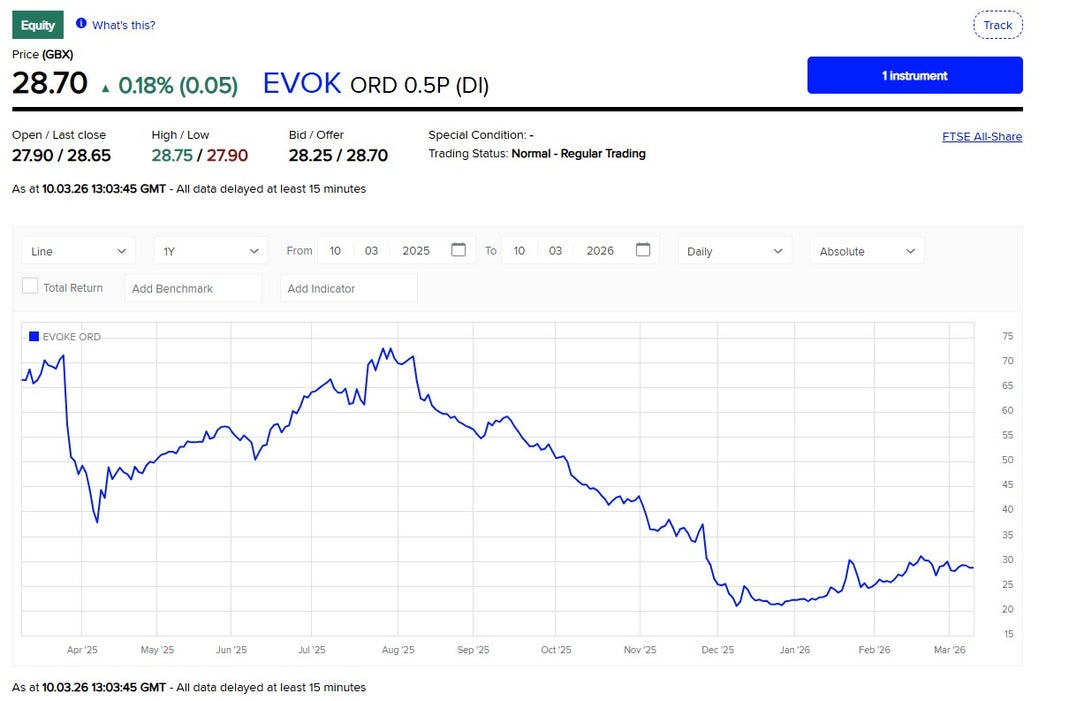
Private equity takeover considered as Evoke faces tax and debt pressure
Evoke has launched a strategic review as new UK gambling tax increases and rising debt put pressure on the business. Analysts suggest a private equity takeover or asset sales could be among the operator’s possible options.

Entain posts £681m loss after UK gambling tax impact
Entain has reported a £681m loss for 2025 after recording a significant impairment charge linked to UK gambling tax changes announced in the government’s November Budget. Despite the loss, the company said underlying revenue continued to grow.
AI chatbots found recommending illegal online casinos to vulnerable users
AI chatbots operated by major technology companies have been found recommending illegal online casinos and advising users how to bypass gambling safeguards. The findings have prompted concern from regulators, campaigners and addiction experts in the UK.

Curious Games enters iGaming market through Relax Gaming partnership
Curious Games has launched its entry into the iGaming sector through a new partnership with Relax Gaming. The studio will distribute its upcoming titles through Relax’s Silver Bullet programme, gaining access to regulated markets and tier-one operators worldwide.

Why iGaming tech companies are increasingly choosing Edinburgh
Edinburgh is rapidly establishing itself as one of Europe’s leading iGaming technology hubs. Industry figures say the city’s fintech expertise, world-class universities and growing network of operators and suppliers are attracting companies seeking engineering, data science and AI capabilities.

Texas Primary Election Results Hurt Efforts to Legalize Casinos, Gambling
Numerous anti-gambling incumbents defeated pro-gambling challengers who were backed by Las Vegas Sands’ political action committees (PACs).

PrizePicks Exits Canadian Market as Company Prioritizes US Expansion
PrizePicks will end its Canadian operations by April, citing regulatory hurdles and reallocating resources to expansion in the United States.

New Zealand DIA Consults on Baccarat Rule Changes, Including New “Dragon Tiger” Wagers
The Department of Internal Affairs is seeking feedback on proposed Baccarat rule updates, including a new wager variation and clearer table signage rules.

Mountain West Conference, Palms Casino Resort Strike Multiyear Partnership
Palms will now become the Official Hotel Partner of the conference, which includes schools such as UNLV and Nevada, through 2028.

SkyCity Faces Legal Test Over Malta-based Online Casino
SkyCity says it will defend proceedings over losses on SkyCity Online, as a funded class action looks set to test whether the Malta-based model was lawful for NZ players.

Six Flags to Sell Seven Theme Parks to EPR Properties for $331 Million
Six Flags is selling seven amusement parks to EPR Properties in a $331 million deal aimed at focusing on higher-performing locations.

Gambling Commission chief Andrew Rhodes set for consultancy role after regulator exit
Outgoing Gambling Commission CEO Andrew Rhodes is reportedly preparing to join a consultancy created by gambling law firm Harris Hagan after leaving the regulator, raising questions about potential conflicts of interest.

Bet365 ends longstanding UK racing sponsorships amid tax pressure
Bet365 has confirmed it will end several long-running horse racing sponsorships, including the Craven Meeting and major Haydock fixtures, citing growing tax and regulatory pressures facing UK betting operators.
BGC launches Spot the Black Market campaign amid illegal gambling concerns
The Betting and Gaming Council has launched a new “Spot the Black Market” campaign aimed at helping players identify illegal gambling sites as concerns grow about the size of the UK’s online black market.

Fairfax Casino Bill Approved by House, Almost at Governor’s Desk
If the bill receives final approval, Fairfax County will become eligible for a casino. However, there’s no guarantee that one will be constructed.

Verizon Considered Exiting $1 Billion NFL Sponsorship Amid Cost-Cutting Efforts
Verizon evaluated pulling back from its NFL sponsorship while reviewing hundreds of millions in sports and music partnerships.

Top UK gamblers spend £745 a month as betting activity rises ahead of major sports events
New data from Nationwide shows gambling spending rising in the UK, with the top 10% of gamblers wagering an average of £745 per month. The findings come ahead of a busy year of major sporting events expected to drive further betting activity.

Kambi Strengthens OLG's Sportsbook in Ontario's Competitive Market
Kambi enhances OLG's sportsbooks with advanced tech, seamless retail integration, and strong regulatory compliance to compete in Ontario.
Bet St George launches UK betting brand ahead of Cheltenham Festival
A new bookmaker has entered the UK market just weeks before the Cheltenham Festival, promising a data-driven approach inspired by the medical sector.

Meta Allows Illegal Crypto Gambling Ads to Run Despite ACMA Warning
The Guardian says Instagram posts promoting offshore crypto casino Rainbet stayed up despite user reports, even as ACMA warned influencers about major fines.

PokerStars Launches in Ontario Through FanDuel Partnership
PokerStars is set to launch in Ontario through an exclusive FanDuel partnership, with cross-border pool liquidity and legal challenges.

DraftKings Merges Casino, Sports Betting, Predictions in Unified Super App
Customers will be able to place sports bets, purchase prediction contracts, access the lottery, and play online casino games in the same app.

Paramount Plans HBO Max–Paramount+ Merger After Warner Bros. Deal
Paramount plans to merge HBO Max and Paramount+ following its Warner Bros. deal, potentially creating a 200M-subscriber streaming giant.

Ealing Council launches consultation on 2026 gambling policy
Ealing Council has launched a consultation on its draft 2026 Gambling Licensing Policy, covering 148 premises across the borough and introducing a new local area profile to assess gambling harm risks. Residents and businesses have until 22 March 2026 to respond.

Ireland’s iGaming Reset Tests Strength of New Regulator
Ireland’s long-awaited gambling overhaul is now live. With betting licence applications open and the Gambling Regulatory Authority of Ireland fully operational, operators are weighing fresh opportunities against tougher compliance, advertising limits and personal liability risks.

Bodog Transitions to Ozoon Amid Regulatory Changes in Canada
Bodog exits Canada, rebranding as Ozoon, transferring all player accounts while adapting to tightening provincial gambling regulations.

Can the DOJ Break Up Live Nation and Ticketmaster? Antitrust Trial Begins
The DOJ’s antitrust trial against Live Nation begins, with claims that the company dominates the concert industry and harms fans and venues.

Warner Bros. Employees Worried About Potential Job Losses With Paramount Merger
Current Warner Bros. Discovery employees fear job loss with Paramount merger.

Paramount Wins Warner Bros. Discovery Bidding War as Netflix Walks Away
Paramount secures Warner Bros. Discovery after Netflix exits the bidding.


